Introduction
In this
post I have tried to explain how to setup and configure Apache hadoop cluster with 2 or more nodes in a standalone
machine probably ur windows laptop or desktop. This will help you to build map reduce program and run in a
real cluster like environment and will help you to understand hadoop better.
Apache hadoop is a free open source software release for reliable
and scalable distributed computing. It is a framework that allows for
distributed processing large data sets across clusters of computers.
During this hadoop cluster setup, at high level the
following activities will be performed
v
Creating base nodes for the cluster
v
Setting up base operating system for the cluster
v
Setup hadoop
dependencies in the nodes
v
Configure hadoop users
,access
v
Setup authenticity across the cluster nodes
v
Configure hadoop roles
for the nodes
v
Run hadoop daemons for
each roles
v
Browse for hadoop hdfs and job tracker sites
Creating base nodes
for the cluster:
If you are planning
to try out this setup on your local windows laptop or desktop, download VMware
player which is a free tool that can help you with setting up virtual
machines with their local IP, so at the end you have a simple network of
servers that can talk to each other. Nowadays laptop are
coming with multiple cores and 4 GB of Memory, so it is easy to setup at least
3 nodes in your personal laptop or desktop.
Setup a Linux flavor
of OS in the base nodes:
On the base VM nodes
you have set with VMware player, you can install a linux
based OS with a ISO file, I choose ubuntu server as
the OS, it is available free to download
. Download
the ISO and complete the VM creation with the VM Player.
Once the OS
installation is done, you will be ended with a root or sudo
user for the server. You can get the IP address of the servers by typing the
command ifconfig , note down the IP addresses for the servers.
Setup Hadoop and its dependencies:
We have the servers
setup with OS and a sudo user to operate on,now we can start setting up hadoop in the nodes.
Apache hadoop has the following dependencies
1.
Java version 6 or higher
2.
SSH
Download and set up in the server, I setup up JRE under a folder
/opt/jre1.6.0_45 and set Java Home under ~/.bashrc ,
you can verify the setup by typing the command Java -version and check the
version details displayed.
SSH can be
installed by using the command - sudo apt-get install openssh-server
Verify SSH by
executing the command SSH localhost to that machine itself.
Download a stable
version of
hadoop . I choose
1.0.X as the version to setup.
If you have downloaded
the .tar.gz file you can use the command tar -zxvf
{file.tar.gz} to unzip the contents. I have set it to the location /opt/hadoop-1.0.4 .
Configure Hadoop
We have hadoop and its dependencies
set, we can now start configuring hadoop in that server,
this involves the following activities
1.
Create a new user , say hadoop,
In Ubuntu I used the command Adduser #user
2.
Add the sudo access to
the user by editing /etc/sudoers file , this can be achieved by the following
commands
a. sudo visudo
add the line in the file hadoop ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
3.
Add full permission for this hadoop user to
/opt/hadoop-1.0.4 where we have the hadoop binaries folder installed , this can
be done by the following commands
a. Chown –R hadoop:hadoop
b. Chmod –R 777 hadoop-1.0.4
You have to repeat the above steps for all the nodes in the
cluster or simply clone the virtual machines but make sure each virtual machine
has got different IP Address. Consider you have created 3 nodes for this cluster.
Now we have 3 nodes created, we have to decide on the roles
of the nodes considering one node to be master node playing roles of namenode and jobtracker and other
nodes playing datanode and tasktracker,
we can call the nodes as hdpMaster, hdpSlave1,
hdpSlave2.
Configuring
authenticated SSH access between master and other nodes
We need to configure
authenticated SSH access (password less) for hadoop
user from masternode to rest of slavenodes.
Perform the following steps to setup the same.
$ssh-keygen
-t rsa (
generates the key file)
Copy the key file to all the slave
machines
$scp .ssh/id_rsa.pub
hadoop@192.168.8.129:~hadoop/.ssh/authorized_keys
(Slave1)
$scp .ssh/id_rsa.pub
hadoop@192.168.8.130:~hadoop/.ssh/authorized_keys
(Slave2)
You
should also able to ssh
without password into the same, otherwise you have to do the following to do
the same.
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_dsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Once
the key is added to authorized keys of master,
password less access to machines will be possible.
Verify
whether you are able to connect using ssh
to localhost and all the slaves by using ssh command
ssh localhost
ssh slave1IP
ssh slave2IP
HostEntry for the Server:
Update the
host file with hostnames at etc/hosts
, if you want to call the servers with hostnames
Configure hadoop roles for master and slaves:
We have all
set for the hadoop to start,
we are at the last step of configuring the roles for the nodes and start the
cluster.
In the master
node, perform the following steps
1.
Go to the HadoopHome \
Conf location
2.
Update hadoop-env.sh with JAVA_HOME location to
the Java installation path
3.
Update core-site.xml to the following
4.
Update hdfs-site.xml to the following
5.
Update mapred-site.xml to the following
6.
Update masters file with the masterhostname
7.
Update slaves file with all slavehostname.
Repeat step 1 -4 to all the
slave nodes.
Hadoop
cluster is now configured for hdfs and mapreduce. We can start the corresponding daemons on the
cluster
Step 1 :
go to HadoopHome location
Step 2: Format namenode by running the command bin/hadoop
namenode –format
Step 3: go to bin folder, Run namenode, datanode daemons , Run Jobtracker, tasktracker daemons
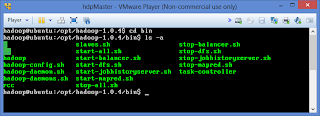
Option 1: Run ./start-all.sh in
master node, this will start all the daemons in all the nodes cluster as
configured in masters,slaves
file
Option 2: Run ./start-dfs.sh in
master node, this will start namenode and datanodes ,
Run ./start-mapred.sh , this will start jobtracker
and tasktracker in the nodes.
Option 3:Run
the following
In Master
node
./hadoop-daemon.sh start namenode
./hadoop-daemon.sh
start jobtracker
In Slaves
node run
./hadoop-daemon.sh
start datanode
./hadoop-daemon.sh
start tasktracker
You can check the logs of the
nodes or any errors during initialization under HadoopHome/logs
in each of the nodes.
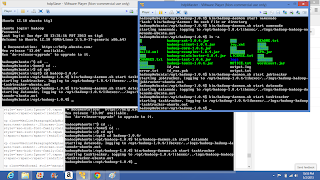
If everything went fine, you
should be able to see the following sites for tracking hdfs
and hadoop jobs
http://masternode:50070/dfshealth.jsp
- to track hdfs and its health
http://masternode:50030/jobtracker.jsp
- to track job running and its status
Reference :
Apache hadoop cluster setup













